Data is everywhere, and businesses, governments, and even individuals are finding new ways to use it each day. But what is data analytics, and why has it become so essential in today’s world? In simple terms, data analytics refers to the process of examining raw data to find patterns, draw conclusions, and support decision-making. Whether you are looking to grow your business, improve your health, or optimize any process, data analytics can help you uncover insights that would otherwise remain hidden.
Let’s break it down further: data analytics involves collecting, cleaning, analyzing, and interpreting data to solve problems or answer important questions. With the explosion of digital information, it has become a crucial tool for many fields, from marketing and finance to healthcare and sports. In this guide, we’ll explain what data analytics is, describe its key processes, and show you the kinds of questions it can help answer.
What are the main steps in the data analytics process?
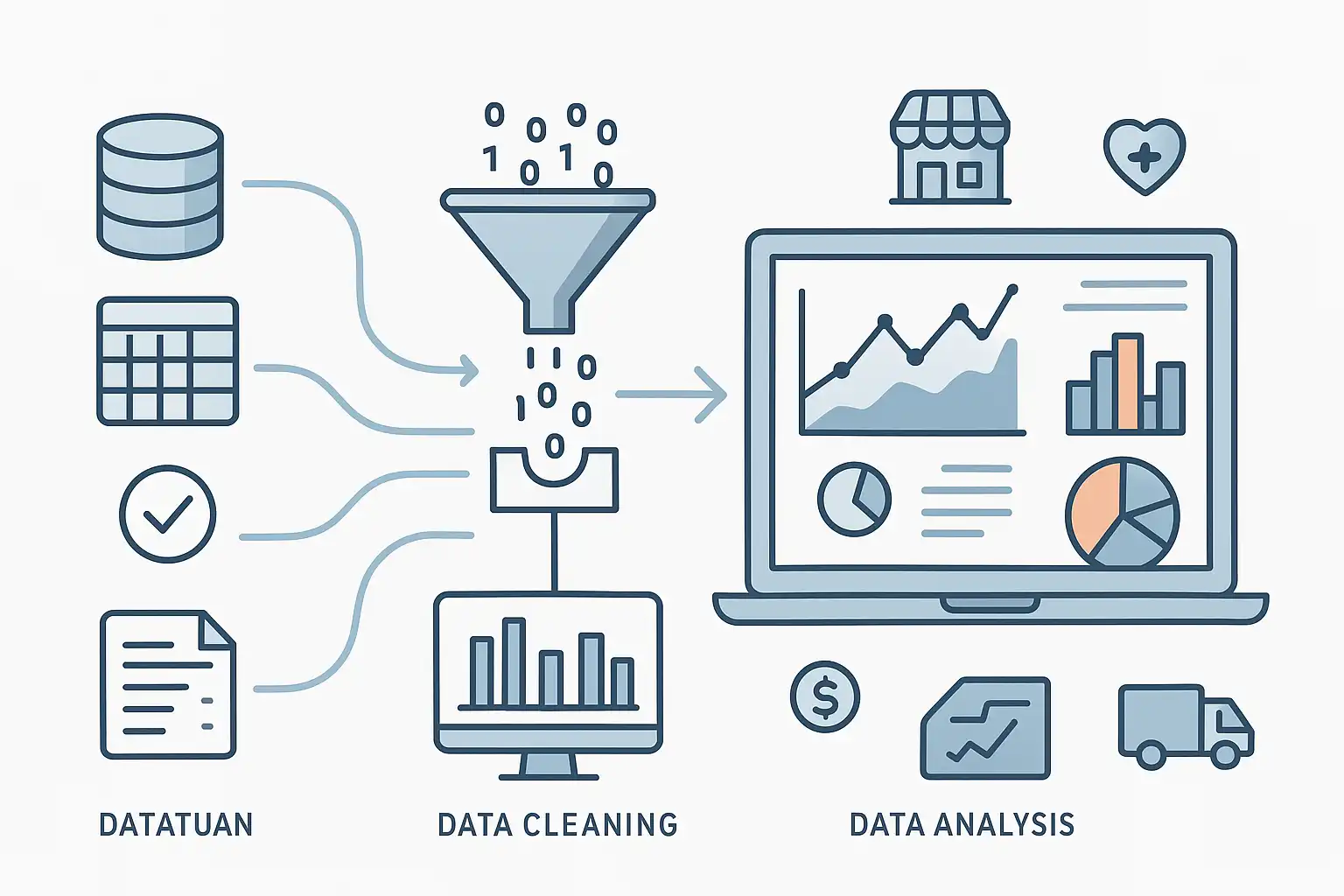
The journey from raw information to actionable insights is systematic. You don’t just look at numbers and hope for answers—you follow a series of logical steps. Here’s an overview of the typical data analytics process:
- Define the Problem: Start by clearly stating the question you want to answer or the problem you need to solve. This might sound simple, but getting this step right is crucial. Your analysis will only be as useful as the question you ask.
- Collect Data: Gather all relevant information. This could come from internal systems, public datasets, customer surveys, sensors, or even social media feeds. Ensuring accurate and comprehensive data at this stage is vital.
- Clean the Data: Raw data is often messy. You need to correct errors, handle missing values, remove duplicates, and standardize formats. This makes your data reliable and prepares it for effective analysis.
- Analyze the Data: Now comes the core of data analytics. Using statistical methods, visualizations, or machine learning algorithms, you start to look for patterns, relationships, and trends.
- Visualize the Results: Numbers alone can be hard to interpret. Charts, graphs, and dashboards make complex data easier to understand. This step helps highlight key findings and presents them in a way everyone can grasp.
- Interpret and Make Decisions: Finally, you use your findings to draw conclusions and suggest next steps. This is where data transforms into real-world actions, shaping policies, strategies, and improvements.
If you want even more details on these stages, exploring resources about the data science workflow can help you see best practices in action and understand how each part fits together.
Why is data analytics important for businesses?
Data analytics is not just a buzzword—it is a powerful driver for smarter business decisions. Modern organizations collect enormous amounts of information about customers, operations, markets, and more. But data alone does not add value. It’s the analysis, interpretation, and action upon that data that make the difference. Here’s how data analytics empowers businesses:
- Informed Decision-Making: By analyzing trends and relationships, organizations can make decisions based on evidence, not just gut feeling.
- Operational Efficiency: Data helps spot bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and save resources.
- Customer Understanding: By segmenting customers and tracking behavior, businesses can tailor products, services, and communications to match needs.
- Risk Management: Analytics can reveal hidden risks, helping teams take action before issues become costly problems.
- Innovation: Discovering patterns and emerging trends opens doors to entirely new products and business models.
For example, in retail, analyzing purchasing data can uncover which products are hot sellers, what promotions work, or when customers are most likely to buy. In healthcare, analytics can reveal which treatments lead to better outcomes for certain groups of patients.
Many small companies might wonder if data analytics is only for large corporations. In fact, small‑business analytics plays a huge role in helping startups and local businesses compete with bigger players. With the right approach, even modest datasets can yield powerful insights.

How does data cleaning improve accuracy in analytics?
One of the most overlooked—but vital—parts of data analytics is cleaning and preparing your data before analysis. Why is this so important? Imagine trying to build a house with warped bricks and bent nails; no matter how skilled you are, the result won’t be solid. The same is true for analytics. Clean, consistent data is the foundation for reliable conclusions.
Data cleaning involves several key tasks:
- Handling missing or incomplete data, either by filling in gaps, removing faulty records, or using specialized methods to estimate missing values.
- Standardizing formats, such as making sure all dates are in the same style or currencies use the same units.
- Removing duplicates—so each unique event or observation is counted only once.
- Converting data types, like making sure numbers aren’t stored as text, which can lead to errors down the line.
Thorough data cleaning reduces the risk of misleading results and helps analysts trust that the patterns they see are real, not just artifacts of bad data. This is especially important if you’re using automated tools or machine learning models, as even small errors in the original data can lead to big mistakes in predictions or decisions.
What types of questions can data analytics answer?
One of the most exciting aspects of data analytics is the sheer variety of questions it can tackle. From everyday business decisions to complex scientific challenges, data analytics helps unlock answers that were once impossible to find. Let’s look at some examples from different industries:
- Retail: What products are most popular among different customer groups? How effective are specific promotional campaigns in driving sales? Which stores or locations perform best and why?
- Healthcare: What treatments lead to the best outcomes for patients with certain conditions? Are there early warning signs of disease that show up in patient data? How can resources be allocated to maximize impact?
- Finance: Which investments are likely to deliver the best returns? What patterns might indicate fraud or other risks? How are spending trends changing over time?
- Transportation: What routes are most efficient for deliveries? How do weather or traffic patterns affect punctuality? Who are the passengers most at risk during emergencies?
- Manufacturing: What are common causes of defects or breakdowns? How can production lines be adjusted to increase output? Where are the biggest opportunities for cost savings?
Clearly, the range is broad. But in general, there are three main kinds of questions data analytics can answer:
- Descriptive: What happened? For example, “How many new customers joined last month?”
- Predictive: What is likely to happen? For example, “Which customers are most likely to cancel their subscriptions?”
- Prescriptive: What should we do about it? For example, “What is the best promotion to offer to keep customers engaged?”
These types of questions are asked across all sectors, reflecting the versatile power of data analytics. For organizations tackling tough challenges, seeking guidance from Expert Data Analytics Solutions can ensure that complex questions are addressed efficiently and accurately.

What tools and techniques are used in data analytics?
Technology has transformed the way we handle and analyze information. There are countless tools available to support every stage of the data analytics process, from basic spreadsheets to sophisticated artificial intelligence platforms. Here are some of the most common types of tools and techniques:
- Spreadsheets: Tools like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets are common starting points for simple analysis and visualization.
- Statistical Software: Programs like R and SAS can handle more advanced computations and modeling.
- Programming Languages: Python is especially popular for data science, offering libraries for cleaning, analysis, and machine learning.
- Business Intelligence Platforms: Tools like Tableau or Power BI turn complex datasets into interactive dashboards and visual reports.
- Machine Learning Libraries: Popular options such as scikit-learn or TensorFlow can automate prediction and classification tasks.
- Database Systems: SQL databases store and manage large volumes of structured data efficiently.
Choosing the right tool depends on the problem, your team’s skills, and the available data. To get the most from your data, it helps to match your needs to the right set of technologies. For small companies and startups, using tailored Data Analytics Tools for Small Business can make sophisticated analytics accessible, even with limited resources.
How does data visualization help people understand analytics?
Even the most thorough analysis can be hard to communicate if it’s buried in numbers. That’s where data visualization comes in. By turning raw figures into clear, appealing visuals—like charts, graphs, and maps—data visualization makes complex ideas easy to grasp.
Some advantages of effective visualization techniques in data analytics include:
- Making trends and patterns obvious at a glance.
- Revealing outliers or unusual observations that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- Allowing different audiences—from executives to frontline staff—to quickly understand important findings.
- Supporting storytelling, so data can be used to persuade or inform more effectively.
Popular visualization types include bar charts for comparing groups, line graphs for trends over time, scatter plots for showing relationships, and heat maps for highlighting concentrations or intensities. Many business intelligence platforms now offer drag-and-drop visualization tools, helping anyone—even those without a technical background—create informative visuals.
What are some real-world examples of data analytics in action?
Data analytics is not just for big companies or tech giants. It’s used every day by organizations of all sizes to make better decisions. Here are a few real-world examples:
- Marketing Campaigns: Companies analyze customer data to segment their audience and personalize offers, leading to higher engagement and better sales results.
- Healthcare Improvements: Hospitals use analytics to identify which treatments speed up recovery times, helping set best practices and save costs.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Logistics firms examine delivery times and routes to minimize delays and reduce expenses.
- Sports Analytics: Teams analyze player performance data to make strategic decisions on training, player selection, and in-game tactics.
- Education: Schools assess student data to identify those who may need extra support, tailoring teaching methods to individual needs.
Each of these cases shows how analytics delivers practical benefits, turning raw data into positive action. From predicting demand to catching fraud, the possibilities are constantly expanding as new tools and data sources emerge.
What are the challenges of implementing data analytics?
While the benefits of data analytics are clear, making it work in practice can be challenging. Common hurdles include:
- Data Quality: Incomplete, inaccurate, or inconsistent data can lead to faulty conclusions.
- Integration: Combining information from different sources or formats can be complex and time-consuming.
- Skills Gaps: Not every organization has experienced data analysts, so building capability takes investment.
- Privacy and Security: Protecting personal and sensitive data is critical, especially as regulations become stricter.
- Change Management: Encouraging teams to trust data-driven methods can require a cultural shift within an organization.
Despite these challenges, the rewards make it worthwhile. Many organizations find that starting small—using a single project or department as a test case—helps show value and build momentum.
How can you get started with data analytics?
If you’re new to data analytics, getting started might feel intimidating. The good news is, you don’t have to be a mathematician or programmer to make progress. Here are steps you can follow to start unlocking the value in your data:
- Define a specific question or goal that matters to your organization.
- Identify the data you already have and consider what additional information might be helpful.
- Start simple—use Excel or other familiar tools to explore basic summaries and visualizations.
- Clean up your data to correct any obvious errors or gaps.
- Seek out beginner-friendly resources, online courses, or communities where you can ask questions and share ideas.
- Don’t be afraid to experiment. Try visualizing your findings or sharing them with colleagues to spark more insights.
As you gain experience, you can explore more powerful tools and advanced techniques. Over time, building a data-driven mindset across your team can lead to better decisions, greater efficiency, and new opportunities.
What is data analytics: answers to your top questions
While both fields focus on making sense of data, data analytics is mainly about examining existing data to solve a specific problem or answer a question. Data science is broader—it can involve building new analytical methods, predictive models, and sometimes includes skills in programming, statistics, and domain expertise. You can think of data analytics as one important part of the broader data science workflow.
Yes. With the right tools and setup, data analytics can provide insights as soon as new information is available. Real-time dashboards and automated alerts help organizations react quickly, whether tracking sales, monitoring system health, or responding to customer feedback instantly.
No, any organization can benefit from data analytics. Even small businesses with limited data can uncover valuable trends and opportunities, and many affordable tools are designed with their needs in mind. The key is to start with a clear question and use the tools that best fit your resources and goals.
Start by exploring free online tutorials, enrolling in beginner courses, or reading books designed for non-technical audiences. Practicing with real data—like your business’s sales history or publicly available datasets—can boost your understanding. Remember, curiosity and a willingness to experiment are as important as technical skills when starting your journey in data analytics.
