BI analyst salary by state: where the highest-paying markets are
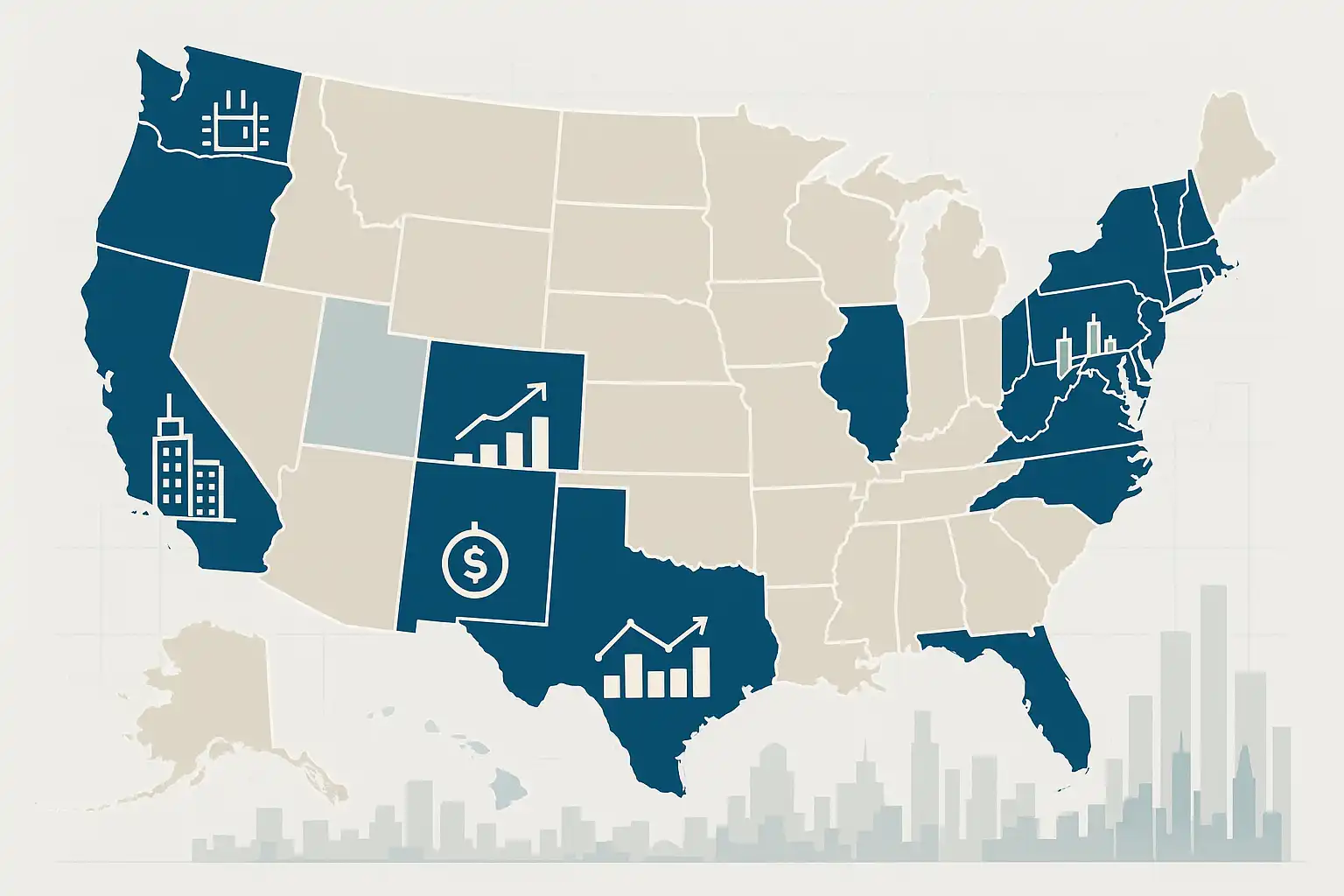
Business Intelligence (BI) analyst salaries vary significantly across U.S. states, influenced by cost of living, industry presence, experience, and company size. As of May 2024, the highest-paying states for BI analysts are California ($107,052), New York ($105,549), Washington ($104,098), New Jersey ($102,505), and Texas ($101,952). These states benefit from strong tech and finance sectors that drive demand and higher wages. While cost of living often dictates salary levels, states like Texas offer competitive pay with lower living expenses, enhancing purchasing power. Lower-paying states in the Midwest and South typically have smaller tech markets but offer a better cost of living balance. High-paying BI roles usually require advanced skills in tools like Power BI, Tableau, SQL, Python, and cloud platforms. Certifications and experience in data visualization and predictive analytics further boost earning potential. Remote BI positions may adjust pay based on the candidate’s location, while salary negotiations should consider total compensation and market trends. Ultimately, balancing salary with living costs and career growth opportunities is crucial for maximizing BI analyst compensation and quality of life across different states.